Ad Blocker Detected
Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors. Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
A leukemia patient has a relative who wishes to donate blood for a transfusion. Which of the following medical conditions would disqualify the donor?

Hepatitis C is a viral infection spread through bodily fluids, leading to liver inflammation. People with hepatitis C are generally prohibited from donating blood due to the high risk of transmitting the infection to the recipient.
A patient hospitalized with myocardial infarction develops severe pulmonary edema. Which symptoms should the nurse anticipate?

Pulmonary edema leads to symptoms such as air hunger, anxiety, and agitation. Additional signs may include coughing up blood or frothy blood, difficulty breathing while lying down, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.
A patient with a history of diabetes mellitus is on the second postoperative day following cholecystectomy. She complains of nausea and is unable to eat solid foods. The nurse finds her confused and shaky. What is the most likely cause of her symptoms?

A postoperative diabetic patient who cannot eat is likely experiencing hypoglycemia. Symptoms such as confusion and shakiness are common. A lack of glucose in the brain (neuroglycopenia) can lead to confusion, concentration difficulties, irritability, hallucinations, focal impairments (e.g., hemiplegia), and, if left untreated, coma and death.
A nurse begins her medication rounds and encounters a non-verbal 4-year-old boy with no identification. What action should the nurse take?

n this situation, the child’s identity can be confirmed based on the father’s statement. The medication should not be withheld after confirming the child’s identity.
A nurse is giving a Vitamin K injection to a 30-day-old infant. What is the most suitable injection site?
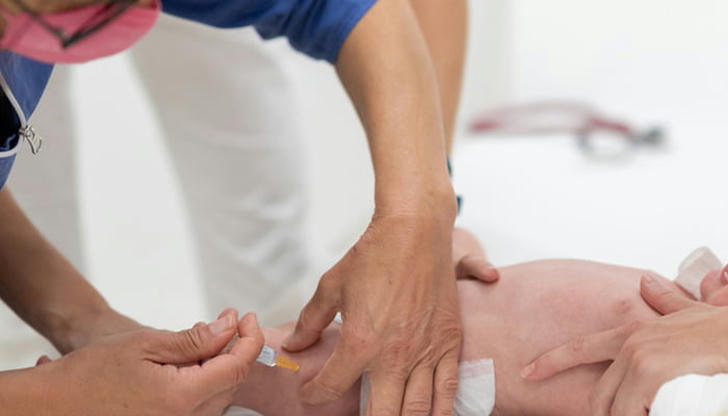

Medications should be injected into the thickest part of the vastus lateralis muscle, which is located at the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the thigh.
A child is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of stage II Wilms tumor. Which statement accurately describes the characteristics of this stage?

Stage II of Wilms tumor refers to the tumor spreading beyond the kidney but being entirely removable through surgery.
A 30 kg child presents with severe itching due to an allergic reaction from an insect bite. The doctor prescribes 25 mg of diphenhydramine (Benadryl) three times daily. The recommended pediatric dosage is 5 mg/kg/day. How does this prescribed dose compare to the recommended dose?
The prescribed dosage is 25 mg three times a day, but the correct dosage should be 50 mg three times a day, based on the weight-based calculation.
A patient is hospitalized with a diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism. When checking the lab results, which laboratory changes would the nurse expect?
The parathyroid glands are responsible for regulating calcium levels in the blood. In hyperparathyroidism, the calcium level in the serum will be elevated. Chronic excess calcium resorption from the bones due to high levels of parathyroid hormone can lead to osteopenia.
A mother asks about her child’s readiness for potty training. Which factor is the most crucial in this process?

Age is not the most important factor in potty training. The child’s overall mental and physical development plays a much larger role.
A 1-month-old infant with a hydrocele returns for a follow-up visit. The scrotum is smaller than at birth, but fluid is still present upon illumination. What action is the physician most likely to suggest?

Hydrocele in infants typically resolves on its own within the first few months of life, and treatment is generally unnecessary.
What is the most common cause of acute glomerulonephritis?
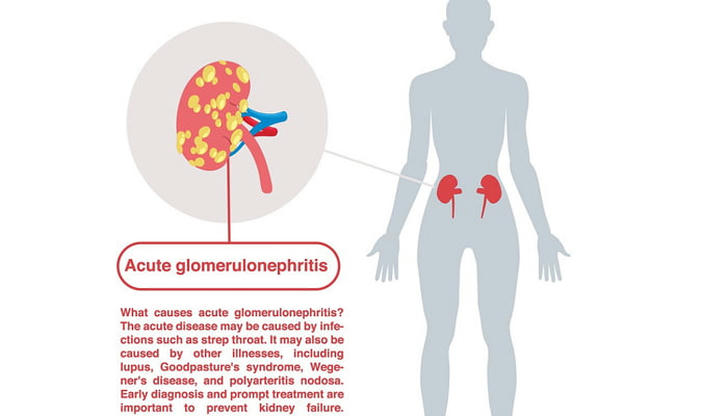
Acute glomerulonephritis is often triggered by an immune response following a recent upper respiratory infection with group A Streptococcus, typically appearing 10-14 days after the infection.
A 28-year-old man is discovered walking in a disoriented manner, appearing sweaty and pale. Which test would likely be conducted first?
For a patient with a history of diabetes, the first step should be to check the blood sugar levels.
A child is treated in the emergency department for scarlet fever. Which of these statements about scarlet fever is incorrect?
A child is treated in the emergency department for scarlet fever. Which of these statements about scarlet fever is incorrect?
A physician diagnoses acute gastritis in a clinic patient. Which medication should be avoided for this patient?
Naproxen sodium, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, can lead to irritation of the upper gastrointestinal tract and is contraindicated in patients with gastritis.
A nurse is assessing a clinic patient diagnosed with hepatitis A. Which route of transmission is most likely in this case?
Hepatitis A is transmitted through the fecal-oral route, often from contaminated food. It is caused by HAV, a single-stranded RNA enterovirus. The virus is primarily acquired through ingestion.
A parent urgently contacts the pediatric clinic after her child ingested cleaning fluid for 20 minutes. What is the nurse’s most important advice?

The poison control center will provide a detailed action plan for handling this child’s situation.
A patient with Addison’s disease seeks nutrition and diet guidance. Which dietary modification should be avoided?

A patient with Addison’s disease needs to maintain normal sodium intake to prevent excessive fluid loss. They should follow a diet with no restrictions on sodium. Those with primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease) require adequate access to salt due to salt-wasting that occurs if left untreated.
A nurse in the emergency department is assessing a patient who had a fiberoptic colonoscopy 18 hours ago. The patient reports worsening abdominal pain, fever, and chills. Which condition should be the nurse’s primary concern?

Bowel perforation is one of the most dangerous complications following a fiberoptic colonoscopy. Symptoms to watch for include worsening abdominal pain, fever, chills, and tachycardia, indicating progressing peritonitis. One of the most severe risks during colonoscopy is the perforation of the colon, which can have high mortality and morbidity rates.
A mother brings her 2-month-old infant to the clinic for a routine check-up and expresses concern because only one testis can be felt in the scrotum. Which statement about an undescended testis is most accurate?

In young infants, it is common for the testes to move and descend naturally by the time they are one year old, so this should be monitored.
A nurse is caring for a patient with peripheral vascular disease (PVD) who reports burning and tingling in the hands and feet, with extreme sensitivity to touch. What is the most likely cause of these symptoms?

Patients with peripheral vascular disease (PVD) often suffer nerve damage due to poor tissue blood flow, which can result in symptoms such as burning and tingling sensations.
After a 4-year-old child falls off a bicycle and sustains head trauma, a nurse in the emergency department is monitoring for signs of increased intracranial pressure. Which symptoms or signs should cause concern?

Frequent vomiting can be an early indication of increased intracranial pressure and demands urgent medical evaluation.
